Difference between revisions of "Module Geometry"
From MohidWiki
PedroChambel (talk | contribs) (explain cartesian top) |
PedroChambel (talk | contribs) |
||
| Line 27: | Line 27: | ||
=== Cartesiantop === | === Cartesiantop === | ||
| − | Cartesiantop is equal to cartesian but builds layers from top to bottom. This type of coodinates are used for Mohid Land. The top is the topography and the bottom is the non-porousmedia (rock). | + | Cartesiantop is equal to cartesian but builds layers from top to bottom. This type of coodinates are used for [[Mohid_Land|Mohid Land]]. The top is the topography and the bottom is the non-porousmedia (rock). |
== Distances == | == Distances == | ||
Revision as of 15:50, 14 April 2009
Contents
Overview
Module Geometry handles the vertical discretization in MOHID. It was designed to divide the water column (in MOHID Water) or the soil compartment (in MOHID Land) in different vertical coordinates: Sigma, Cartesian, Lagrangian, Fixed Spacing, Harmonic, etc. A subdivision of the vertical domain into different sub-domains using different vertical coordinate systems is also possible.
General options
- Minimum depth
Vertical coordinate system
Sigma
Cartesian
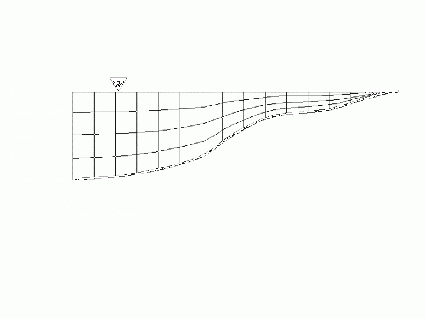
The Cartesian coordinate can be used with or without shaved cells.
Fixspacing
The Fixed Spacing coordinate allows the user to study flows close to the bottom.
Lagrangian
The Lagrangian coordinate moves the upper and lower faces with the vertical flow velocity.
Harmonic
The Harmonic coordinate works like the Cartesian coordinate, just that the horizontal faces close to the surface expand and collapse depending on the variation of the surface elevation. This coordinate was implemented in the geometry module to simulate reservoirs.
Fixsediment
SigmaTop
Cartesiantop
Cartesiantop is equal to cartesian but builds layers from top to bottom. This type of coodinates are used for Mohid Land. The top is the topography and the bottom is the non-porousmedia (rock).
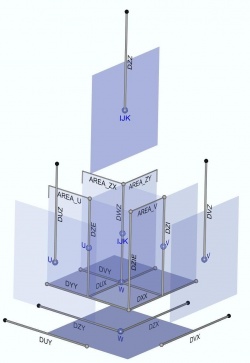
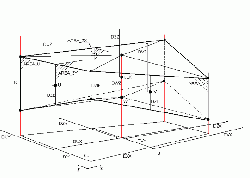
Distances
Public routines
- ModuleHorizontalGrid
- GetHorizontalGrid(HorizontalGridID, XX_IE, YY_IE, XX_Z, YY_Z,XX_U, YY_U, XX_V, YY_V, XX_Cross, YY_Cross, DXX, DYY, DZX, DZY, DUX, DUY, DVX, DVY, XX, YY, XX2D_Z, YY2D_Z, STAT)
- ModuleGeometry
- GetGeometryDistances(GeometryID, SZZ, DZZ, DWZ, DUZ, DVZ, DZI, DZE,ZCellCenter, ActualTime, STAT)
Areas
Volumes
Bathymetry consistency diagnostic
Once the vertical discretization is imposed and the bathymetry is chosen, the bottom layer can yield stability problems when using shaved cells. You can have very thin bottom cell next to a very wide bottom cell. To diagnose the existence of such problematic cells, a geometry diagnostic tool was developed.