Difference between revisions of "Module PorousMediaProperties"
From MohidWiki
PedroChambel (talk | contribs) |
PedroChambel (talk | contribs) |
||
| Line 4: | Line 4: | ||
===Water flow=== | ===Water flow=== | ||
The water movement in soil will be dependent on the pressure gradients existing in the soil profile and also according to gravity. The equation that describes this motion is the Buckingham Darcy equation (Jury et al,1991) (3) where J is the water velocity, h is the pressure head, θ is the water content and K is the hydraulic conductivity. | The water movement in soil will be dependent on the pressure gradients existing in the soil profile and also according to gravity. The equation that describes this motion is the Buckingham Darcy equation (Jury et al,1991) (3) where J is the water velocity, h is the pressure head, θ is the water content and K is the hydraulic conductivity. | ||
| + | |||
<math>a= \sum \left ( \frac{a}{b} \right )</math> | <math>a= \sum \left ( \frac{a}{b} \right )</math> | ||
===Evapotranspiration=== | ===Evapotranspiration=== | ||
Revision as of 16:55, 7 February 2011
Contents
Overview
Main Processes
Water flow
The water movement in soil will be dependent on the pressure gradients existing in the soil profile and also according to gravity. The equation that describes this motion is the Buckingham Darcy equation (Jury et al,1991) (3) where J is the water velocity, h is the pressure head, θ is the water content and K is the hydraulic conductivity.
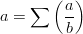
Evapotranspiration
In Figure below it can be seen that the actual transpiration and evaporation are calculated in Porous Media module of MohidLand. The actual evaporation, which happens only at the soil surface, is calculated based on a pressure head limit imposed by the user. It allows the model to not evaporate any surface water, even if it is available, when the soil is very far way from the saturation point.
