Difference between revisions of "Extrapolation"
From MohidWiki
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | Extrapolation is often required when interpolation techniques cannot be used | + | Extrapolation is often required when interpolation techniques cannot be used; often when mapping information from one dataset to a grid. Extrapolation methods vary, yielding different results both in quality and in performance. This article proposes a couple of simple extrapolation techniquesthat use all the information available to extrapolate. The techniques inspire from the weighted average principle. |
==Weighted Average== | ==Weighted Average== | ||
Revision as of 10:32, 10 February 2012
Extrapolation is often required when interpolation techniques cannot be used; often when mapping information from one dataset to a grid. Extrapolation methods vary, yielding different results both in quality and in performance. This article proposes a couple of simple extrapolation techniquesthat use all the information available to extrapolate. The techniques inspire from the weighted average principle.
Contents
Weighted Average
Suppose you have a discrete dataset 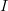 , with coordinates
, with coordinates 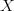 on a normed space, and want to map the dataset to another dataset,
on a normed space, and want to map the dataset to another dataset, 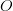 , with a new set of coordinates
, with a new set of coordinates 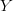 . The operation is performed by constructing mapping coefficients
. The operation is performed by constructing mapping coefficients 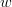 , also called "weights", and by performing a linear combination of the elements of
, also called "weights", and by performing a linear combination of the elements of 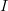 with the weights,
with the weights, 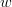 , to compute each element of
, to compute each element of 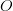 .
.
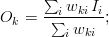
Any method of constructing the weights is valid and depends on the nature of the mapping. A practical use-case consists in performing an interpolation/extrapolation of the data from 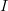 to
to 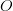 and thus the weights
and thus the weights 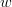 are a function of the coordinates
are a function of the coordinates 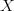 and
and 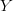 and of the norm of the space.
and of the norm of the space.